CORDIC Accelerator 3: Inverse & Forward Kinematics
Forward kinematics: enables us to compute the end-effector position in global coordinates from given joint angles and link lengths.
The inverse computation ("inverse kinematics") yields the required joint angles given a desired end-effector position.
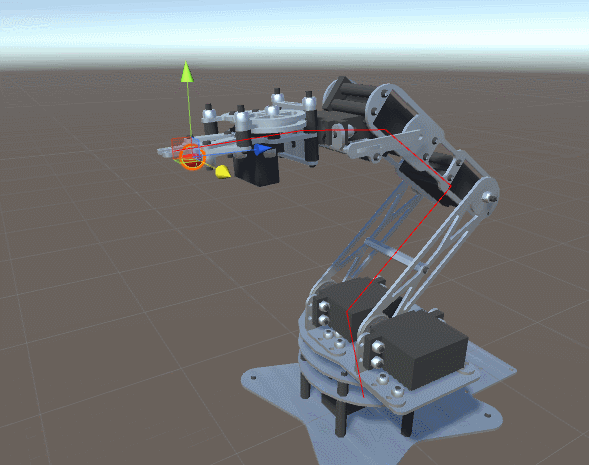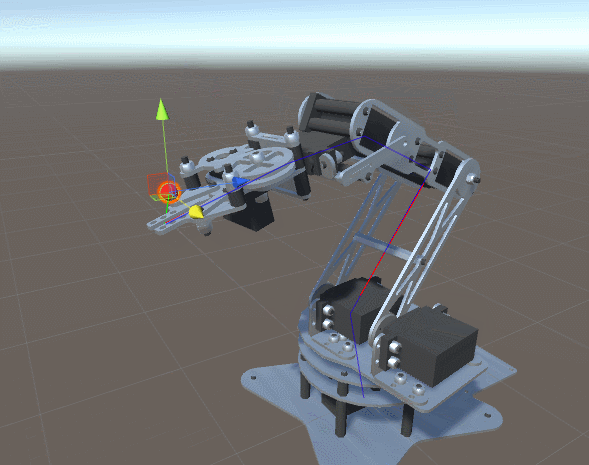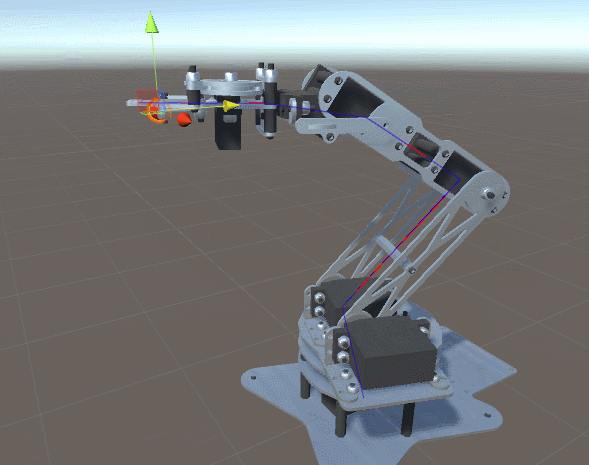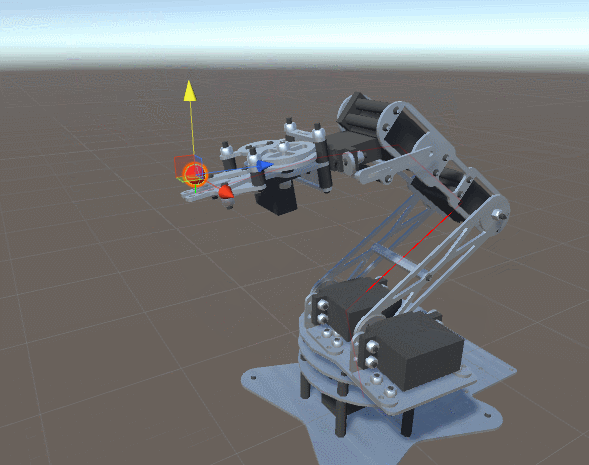
What might prevent the robotic arm in the GIF above from catching the ball? If the ball is moving too quickly, the motors may be physically incapable of rotating fast enough to keep up with it.
But in some cases, the motor properties are not the bottleneck, rather the time it takes to compute the inverse kinematics may introduce significant latency.
This is what we seek to accelerate.
Next: 4: CORDIC algorithms